Contents
Why Does Copper IUD Cause Heavier Periods?
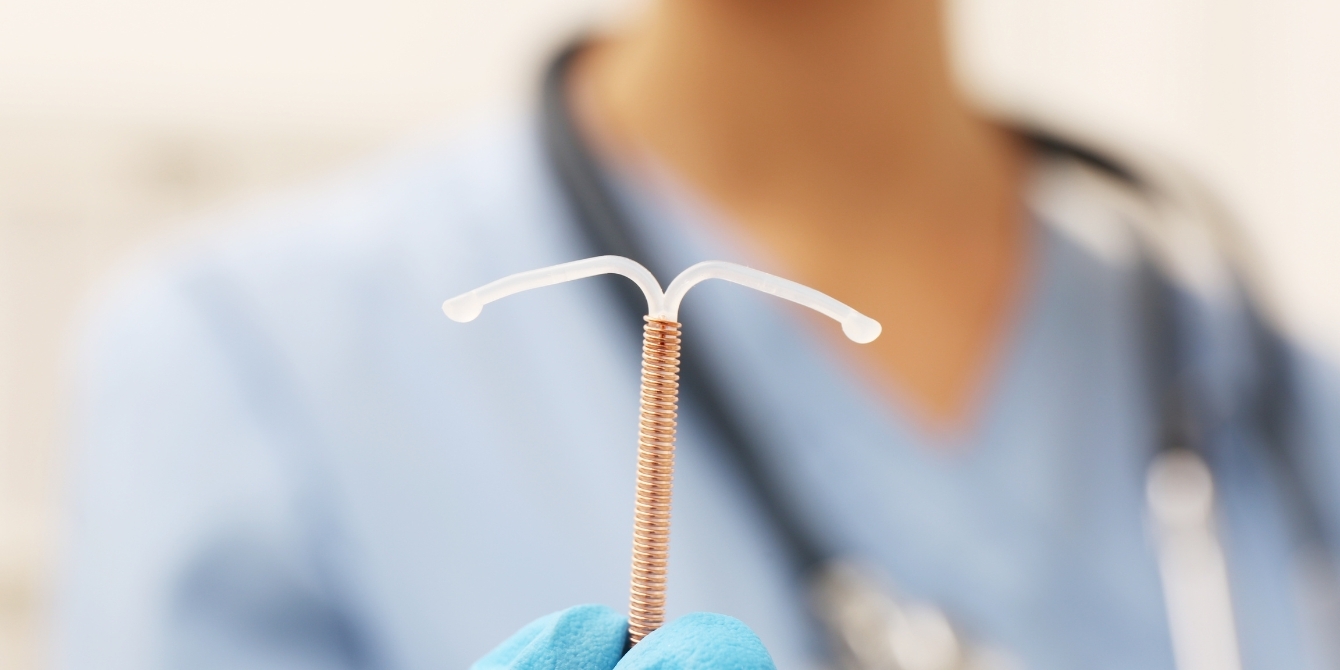
The copper IUD, such as Paragard, is a non-hormonal contraceptive device that releases copper ions into the uterus, creating an environment that is toxic to sperm, thus preventing fertilization. While the copper IUD is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, it can also lead to changes in menstrual bleeding patterns for some individuals.
Here’s a detailed explanation of why the copper IUD may cause heavier periods:
1. Inflammatory Response
The copper IUD triggers an inflammatory response in the uterus due to the presence of copper ions. This inflammation can increase blood flow to the uterus and uterine lining, resulting in heavier menstrual bleeding.
2. Thicker Endometrial Lining
Copper ions released by the IUD may stimulate the production of prostaglandins, hormones that influence the menstrual cycle. This stimulation can cause the endometrial lining to become thicker, leading to heavier periods.
3. Increased Blood Vessel Formation
Copper ions may promote the formation of new blood vessels in the uterus, known as angiogenesis. This increased vascularity can contribute to heavier menstrual bleeding as more blood vessels supply oxygen and nutrients to the thickened endometrial tissue.
4. Menstrual Cramps
Some individuals may experience more severe menstrual cramps with a copper IUD due to the inflammatory response and increased uterine contractions caused by the device. This can result in more intense pain during menstruation.
5. Adjustment Period
While heavier periods are a potential side effect of the copper IUD, they often improve over time. Many individuals experience a gradual reduction in menstrual bleeding and cramping after the first few months of having the IUD inserted.
How Does The Copper IUD Work?
The copper IUD, unlike hormonal IUDs, works in several ways to prevent pregnancy without introducing hormones into your body. Here’s a breakdown of its mechanisms:

-
Sperm Toxicity: The copper coil wrapped around the IUD releases copper ions continuously. These copper ions create a toxic environment for sperm within the uterus and fallopian tubes. The copper ions disrupt sperm motility (movement) and lifespan, significantly reducing their ability to reach and fertilize an egg.
-
Inflammatory Response: The presence of the copper IUD in the uterus triggers a localized inflammatory response. This inflammatory reaction creates an environment less hospitable for sperm and a fertilized egg. The white blood cells involved in the inflammation can also engulf and destroy sperm.
-
Thickened Cervical Mucus: Copper IUDs may also cause changes in the cervical mucus, making it thicker and stickier. This thicker mucus acts as a barrier, further hindering sperm from reaching the egg.
-
Potential Impact on Implantation: While the primary focus is on preventing fertilization, some theories suggest copper might also interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterine lining. The exact mechanism for this is still being researched.
Copper IUDs are highly effective in preventing pregnancy, with a typical failure rate of less than 1% in the first year. This means that less than 1 out of 100 people using a copper IUD will get pregnant each year.
IUDs are reversible: If you decide you want to get pregnant, your healthcare provider can easily remove the IUD, and your fertility will return to normal very quickly.
If you’re considering a copper IUD as a birth control method, it’s important to discuss the potential side effects with your doctor. These can include heavier or more crampy periods, spotting between periods, and potential expulsion of the IUD (although rare).
Other Factors That Can Make Periods Heavy
Several factors can contribute to heavier menstrual bleeding, aside from the use of a copper IUD. Here are some additional factors:

1. Hormonal Imbalance
Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can affect the thickness of the uterine lining and the regularity of menstrual cycles. Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders, can lead to heavier periods.
2. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. Depending on their size and location, fibroids can cause heavier menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, and pelvic pain.
3. Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue that lines the uterus begins to grow into the muscular wall of the uterus. This condition can cause heavier periods, severe menstrual cramps, and pelvic pressure or discomfort.
4. Endometrial Polyps
Endometrial polyps are growths that form in the lining of the uterus. While typically benign, they can cause heavier or irregular menstrual bleeding, as well as bleeding between periods.
5. Blood Disorders
Certain blood disorders, such as von Willebrand disease or platelet disorders, can affect blood clotting and lead to heavier menstrual bleeding.
6. Medications
Some medications, including anticoagulants (blood thinners) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can interfere with blood clotting and contribute to heavier menstrual bleeding.
7. Stress
Stress can disrupt hormone levels and menstrual cycles, leading to changes in menstrual bleeding patterns. Chronic stress may exacerbate existing menstrual symptoms, including heavy bleeding.
8. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease is an infection of the female reproductive organs, typically caused by sexually transmitted bacteria. PID can lead to inflammation, scarring, and damage to the reproductive organs, potentially causing heavier periods among other symptoms.
9. Cancer
While less common, certain gynecological cancers, such as endometrial or cervical cancer, can cause abnormal uterine bleeding, including heavier periods.
10. Genetics
A family history of heavy periods or bleeding disorders may predispose individuals to experiencing heavier menstrual bleeding.
11. Diet and Lifestyle
Poor nutrition, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can also impact menstrual health and contribute to heavier periods.
12. Age
During perimenopause, the transition period leading up to menopause, hormonal fluctuations can cause changes in menstrual bleeding patterns, including heavier periods.
13. Miscellaneous
Other factors, such as obesity, pelvic surgery, or reproductive tract abnormalities, may also influence menstrual bleeding patterns and contribute to heavier periods.
Birth Control Options to Make Periods Lighter
When dealing with heavier periods caused by a copper IUD, exploring alternative birth control options can help manage and lighten your menstrual flow. Here are some options to consider:
- Hormonal Birth Control: Hormonal methods like birth control pills, patches, or hormonal IUDs can regulate your menstrual cycle and potentially reduce heavy bleeding.
- Progesterone Therapy: Progesterone-only birth control methods, such as the mini-pill or hormonal IUDs, can help lighten periods by thinning the endometrial lining.
- Non-Hormonal IUD: Consider switching to a non-hormonal IUD, like the copper-free IUD, if you want to avoid hormones but still desire effective birth control.
- Menstrual Cup Usage: Menstrual cups are eco-friendly and can help you track your menstrual flow while potentially reducing period-related complications.
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy lifestyle practices such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing stress can contribute to overall menstrual health and potentially lighten your periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do heavy periods last with copper IUDs?
Heavy periods can last 12 months after getting a copper IUD, with some women experiencing heavy periods and irregular bleeding for years.
Is it normal to bleed heavily with a copper IUD?
Yes, it is common to experience heavy or prolonged bleeding with a copper IUD, which can lead to method discontinuation.
Why don’t doctors recommend a copper IUD?
Doctors may not recommend a copper IUD for individuals with STIs, recent pelvic infections, or untreated cervical or uterine cancer.
Why are my periods so painful with a copper IUD?
Contrary to previous studies, recent research shows that women using a copper IUD do not necessarily experience worse period pain.
Why do copper IUDs make periods heavier?
Copper IUDs may increase copper ion levels in endometrial tissue, leading to the secretion of VEGF and abnormal uterine bleeding.
I am a medical student with experience and interest in Women’s health and well-being.